To optimize 3D printing, researchers apply machine studying to reduce waste and optimize construction in the course of the printing course of.
3D printing applied sciences are quickly increasing to an increasing number of industries, together with drugs, supplies, meals, aerospace applied sciences and plenty of others, making manufacturing quicker, cheaper, and extra dependable.
Nevertheless, with this manufacturing methodology, there’s usually a scarcity or extra of fabric after printing. If not sufficient is used, the printed object could also be too weak, whereas too excessive a cloth circulation charge ends in imperfections within the printed samples, and wastes cash on manufacturing.
To deal with this problem and make 3D printing extra environment friendly, a analysis crew led by Woo Soo Kim of Simon Fraser College in British Columbia, Canada have augmented the 3D printing course of with in situ management and correction of fabric consumption.
The scientists labored with fused deposition modeling, a 3D printing method that prints samples layer by layer, depositing melted materials within the type of filaments in a predetermined method the place the standard of the printed object relies on the circulation charge of the fabric popping out of a particular nozzle. The optimum charge, nevertheless, could also be completely different at varied phases of the printing course of, and the mistaken selection of charge can result in the aforementioned issues
To robotically management and regulate the fabric circulation charge when printing particular person elements — which within the current examine was a plastic canine bone — the researchers turned to machine studying. Their method makes use of information evaluation to regulate the manufacturing course of to be taught from enter information, establish patterns, and make predictions.
The digital camera that was fastened on the 3D printer recorded the printing course of, and the information was then despatched to the pc for evaluation. The machine studying algorithm skilled to find out whether or not the correct quantity of fabric was being extruded at a given second by the looks of the half was in a position to appropriate the method in actual time if the plastic circulation charge was deemed to not be optimum.
All this works properly on paper, however the scientists wanted to check the effectiveness of their algorithm experimentally. To take action, the crew printed samples at varied circulation charges and located that for preliminary extrusion charges of 60%, 80%, 100%, and 120% of optimum, the fabric circulation charge approached the optimum by the tip of the printing course of.
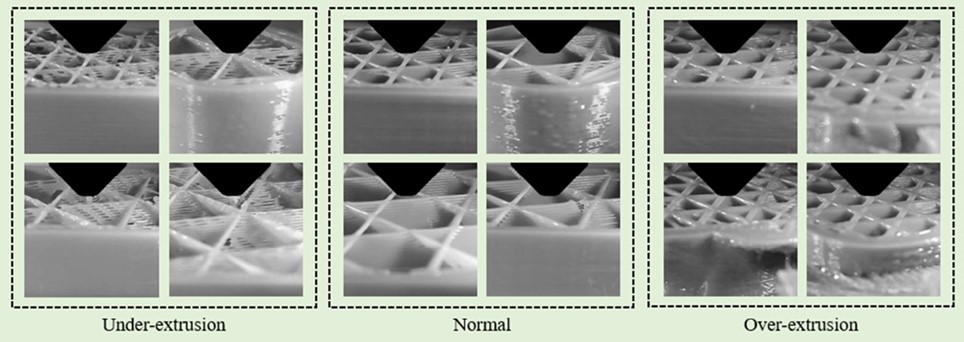
As for the parameters of the printed pattern, the outcomes had been actually spectacular: In comparison with printing with out utilizing the management algorithm, the brand new method resulted in elevated pattern energy by as much as 200%, which can be essential in lots of mechanisms, and saved as much as 40% of the quantity of fabric.
Regardless of the numerous progress, the scientists imagine that additional enchancment of their method is feasible.
First, they imagine that their methodology can be utilized not solely in fused deposition modeling, but additionally with different 3D printing strategies. As well as, not solely might the fabric circulation charge may be managed in actual time, however different parameters of the printing course of, corresponding to temperature of the fabric. Even the printing sample may very well be improved by rising the scale of the information set on which this system is skilled, and by making print high quality checks extra frequent.
As at all times in utilized science, solely additional analysis and their industrial implementation will present whether or not these predictions are appropriate or not.
Reference: Woo Soo Kim, et al., Adaptive 3D Printing for In Situ Adjustment of Mechanical Properties, Superior Clever Techniques (2022). DOI:10.1002/aisy.202200229
Picture credit score: Minku Kang on Unsplash